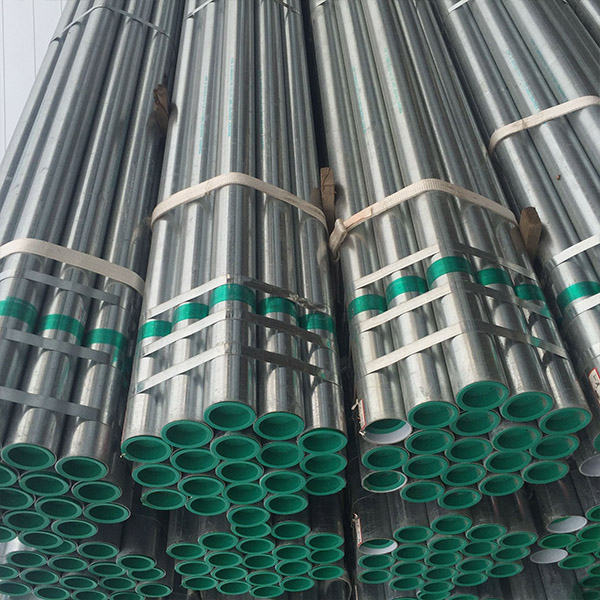
Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipe
Hot-dip galvanized pipe
The hot-dip galvanized pipe is to make the molten metal react with the iron matrix to produce an alloy layer, so that the matrix and the coating are combined. Hot-dip galvanizing is to first pickle the steel pipe. In order to remove the iron oxide on the surface of the steel pipe, after pickling, it is cleaned in a tank with ammonium chloride or zinc chloride aqueous solution or a mixed aqueous solution of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride, and then sent to In the hot dip plating tank. Hot-dip galvanizing has the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion and long service life. The matrix of the hot-dip galvanized steel pipe undergoes a complex physical and chemical reaction with the molten plating solution to form a corrosion-resistant zinc-iron alloy layer with a compact structure. The alloy layer is integrated with the pure zinc layer and the steel pipe matrix, so its corrosion resistance is strong
Cold galvanized pipe
Cold galvanized pipe is electro-galvanized, and the amount of galvanizing is very small, only 10-50g/m2, and its corrosion resistance is much different than that of hot-dip galvanized pipe. Formal galvanized pipe manufacturers, in order to ensure quality, most of them do not use electro-galvanized (cold plating). Only those small enterprises with small scale and outdated equipment use electro-galvanization, and of course their prices are relatively cheaper. The Ministry of Construction has officially announced that cold-galvanized pipes with outdated technology should be eliminated, and cold-galvanized pipes are not allowed to be used as water and gas pipes. The galvanized layer of cold galvanized steel pipe is an electroplated layer, and the zinc layer is separated from the steel pipe substrate. The zinc layer is thin, and the zinc layer simply adheres to the steel pipe base and easily falls off. Therefore, its corrosion resistance is poor. In newly-built houses, it is forbidden to use cold galvanized steel pipes as water supply pipes.



Nominal wall thickness (mm): 2.0, 2.5, 2.8, 3.2, 3.5, 3.8, 4.0, 4.5.
Coefficient parameters (c): 1.064, 1.051, 1.045, 1.040, 1.036, 1.034, 1.032, 1.028.
Note: The mechanical properties of steel is an important index to ensure the final use performance (mechanical properties) of the steel, and it depends on the chemical composition of the steel and the heat treatment system. In the steel pipe standard, according to different application requirements, the tensile properties (tensile strength, yield strength or yield point, elongation), hardness and toughness indexes are specified, as well as high and low temperature properties required by users.
Steel grades: Q215A; Q215B; Q235A; Q235B.
Test pressure value/Mpa: D10.2-168.3mm is 3Mpa; D177.8-323.9mm is 5Mpa
Current national standard
National standards and size standards for galvanized pipes
GB/T3091-2015 Welded steel pipe for low pressure fluid transportation
GB/T13793-2016 Longitudinal electric welded steel pipe
GB/T21835-2008 welded steel pipe size and unit length weight