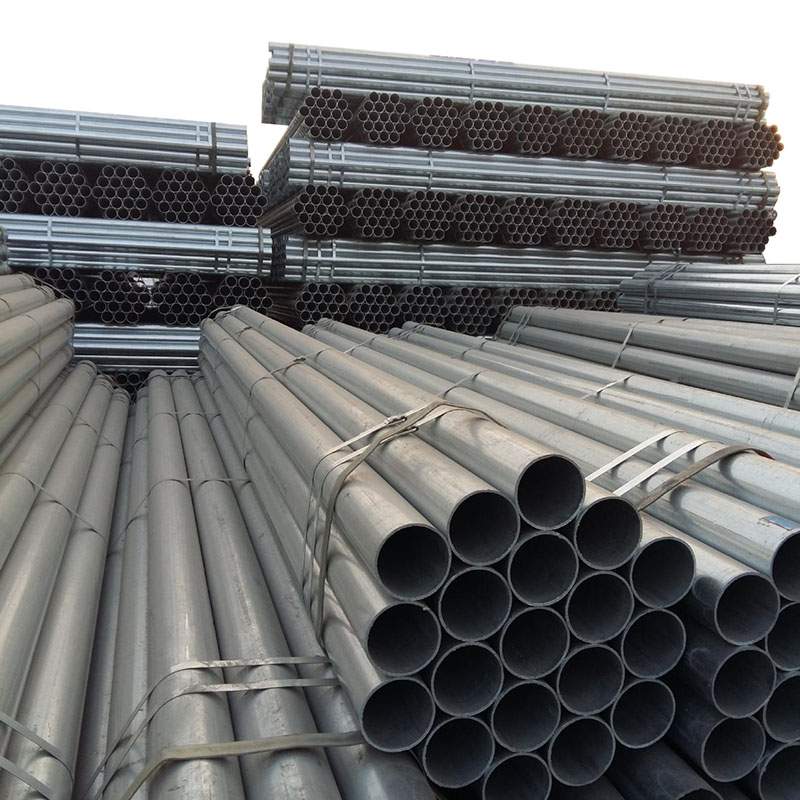
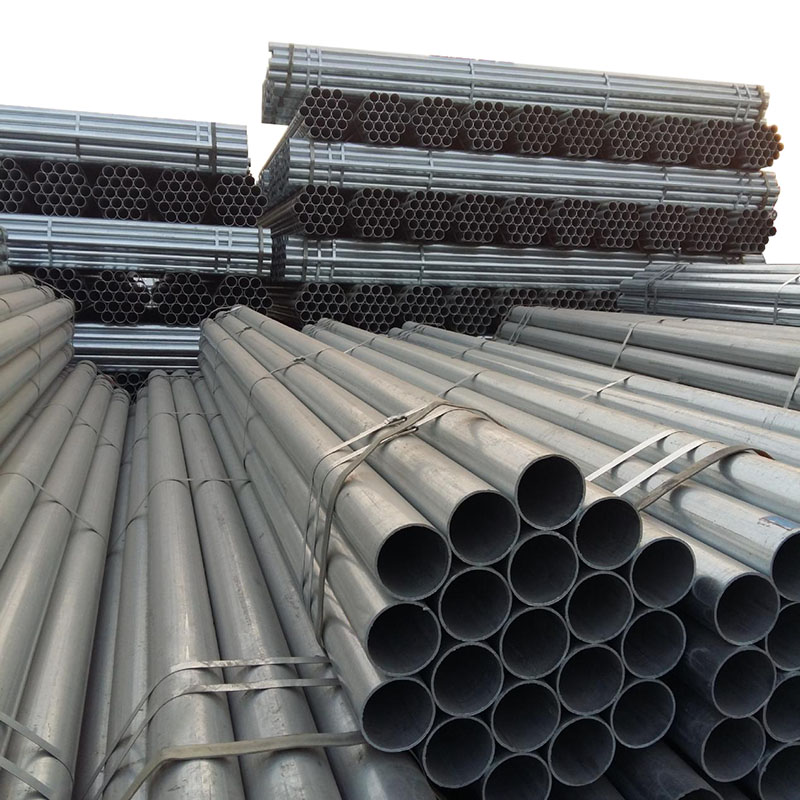
Cold Rolled Color Coated Galvanized Steel Pipe
| Name | Galvanized steel | Intrinsic | Steel |
| Classification | Cold galvanized steel pipe, hot galvanized steel pipe | Scope of application | Construction, machinery, coal mine, chemical industry, electric power, railway vehicle, automobile industry, highway, bridge, container, sports facilities, agricultural machinery, petroleum machinery, prospecting machinery Expand |
| Length | 6m fixed length | ||
| Nominal wall thickness (mm) | 2.0, 2.5, 2.8, 3.2, 3.5, 3.8, 4.0, 4.5 |



1. Tensile strength (σb): The maximum force (Fb) that a specimen undergoes in tension when it is pulled, divided by the stress (σ) obtained from the original cross-sectional area (So) of the specimen, is called tensile strength (σb), in N/mm2 (MPa). It represents the maximum capacity of a metal material to resist damage under tension. Where: Fb - the maximum force the specimen withstands when it is pulled, N (Newton); So - the original cross-sectional area of the specimen, mm2.
2. yield point (σs): metal material with yield phenomenon, the stress when the specimen can continue to elongate without an increase in force (remain constant) during the stretching process, called the yield point. If the force decreases, the upper and lower yield points should be distinguished. The unit of yield point is N/mm2 (MPa). Upper yield point (σsu): the maximum stress before the specimen yields and the force first decreases; Lower yield point (σsl): the minimum stress in the yielding phase when the initial transient effect is not accounted for. Where: Fs - yield force (constant) of the specimen in tension, N (Newton) So - original cross-sectional area of the specimen, mm2.
3. Elongation after break: (σ) In the tensile test, the percentage of the increase in the length of the specimen after pulling off its scale to the length of the original scale is called the elongation. Expressed in σ, the unit is %. Where: L1 - the length of the specimen after the specimen is pulled, mm; L0 - the length of the specimen's original pitch, mm.
4. Fractional shrinkage: (ψ) In the tensile test, the maximum shrinkage of the cross-sectional area at its shrinkage after the specimen is pulled off as a percentage of the original cross-sectional area is called the fractional shrinkage. Expressed as ψ, in %. Where: S0 - the original cross-sectional area of the specimen, mm2; S1 - the minimum cross-sectional area at the shrinkage after the specimen is pulled off, mm2.
5. Hardness index: the ability of a metal material to resist the indentation of a hard object into a surface, called hardness. Depending on the test method and the scope of application, hardness can be divided into Brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness, Vickers hardness, Shore hardness, microhardness and high temperature hardness. For the tube is generally used in Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers hardness three.
Brinell hardness (HB): Using a steel or carbide ball of a certain diameter, press the specified test force (F) into the surface of the specimen, remove the test force after the specified holding time, and measure the indentation diameter (L) on the surface of the specimen. The Brinell hardness value is the quotient obtained by dividing the test force by the spherical surface area of the indentation. Expressed as HBS (steel ball) in N/mm2 (MPa).
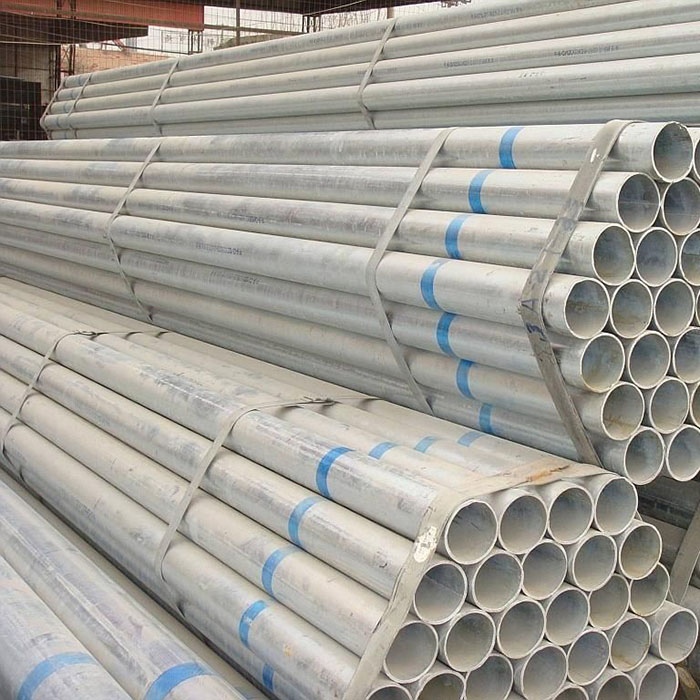
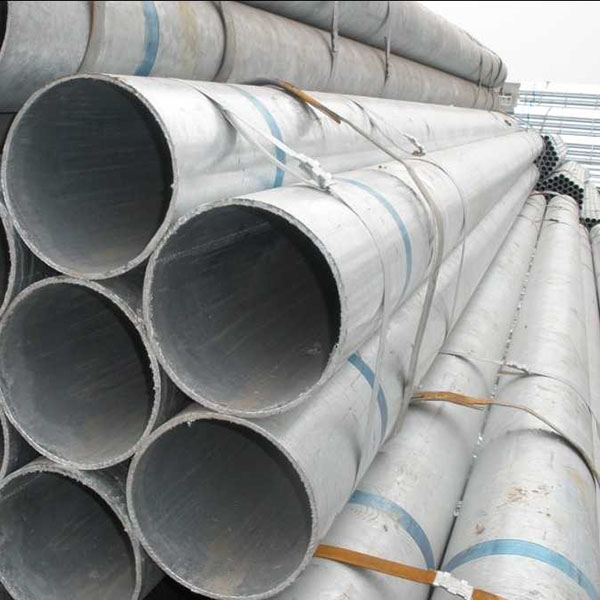
Hot-dip galvanized steel pipes are widely used in construction, machinery, coal mining, chemical industry, electric power, railway vehicles, automobile industry, highways, bridges, containers, sports facilities, agricultural machinery, petroleum machinery, prospecting machinery and other manufacturing industries.
Galvanized steel pipe is a welded steel pipe with a hot dip or electro galvanized surface. Galvanization can increase the corrosion resistance of steel pipes and prolong the service life. Galvanized steel pipe has a wide range of uses, in addition to being used as a pipeline for general low pressure fluids such as water, gas and oil, it is also used as an oil well pipe and oil pipeline in the petroleum industry, especially in the marine oil fields, as an oil heater, condensation cooler and coal distillation and oil washing exchanger for chemical coking equipment, and as a support frame pipe for trestle pipe piles and mining pits, etc.
Water pipe, oil pipe, scaffolding pipe, highway fence, shed cover, etc.
| Nominal inside diameter | Inch | Outer diameter mm | Wall thickness mm | Minimum wall thickness mm | Meter weight kg | Root weight kg | Metre weight kg | Root weight kg |
| DN15 Galvanized pipe | 1/2 | 21.3 | 2.8 | 2.45 | 1.28 | 7.68 | 1.357 | 8.14 |
| DN20 Galvanized pipe | 3/4 | 26.9 | 2.8 | 2.45 | 1.66 | 9.96 | 1.76 | 10.56 |
| DN25 Galvanized pipe | 1 | 33.7 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 2.41 | 14.46 | 2.554 | 15.32 |
| DN32 Galvanized pipe | 1.25 | 42.4 | 3.5 | 3.06 | 3.36 | 20.16 | 3.56 | 21.36 |
| DN40 Galvanized pipe | 1.5 | 48.3 | 3.5 | 3.06 | 3.87 | 23.22 | 4.10 | 24.60 |
| DN50 Galvanized pipe | 2 | 60.3 | 3.8 | 3.325 | 5.29 | 31.74 | 5.607 | 33.64 |
| DN65 Galvanized pipe | 2.5 | 76.1 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 7.11 | 42.66 | 7.536 | 45.21 |
| DN80 Galvanized pipe | 3 | 88.9 | 4.0 | | 8.38 | 50.28 | 8.88 | 53.28 |
| DN100 Galvanized pipe | 4 | 114.3 | 4.0 | | 10.88 | 65.28 | 11.53 | 69.18 |